
1.1 Scrapy 爬虫案例一
Scrapy 爬虫案例:爬取腾讯网招聘信息
案例步骤:
第一步:创建项目。
在 dos下切换到目录
D:爬虫_scriptscrapy_project
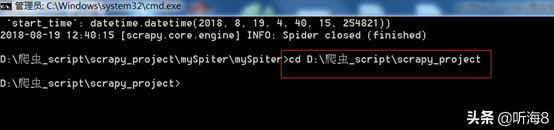
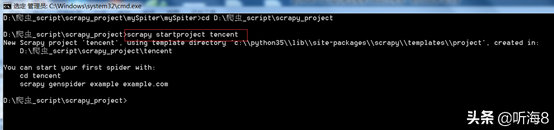
新建一个新的爬虫项目:scrapy startproject tencent
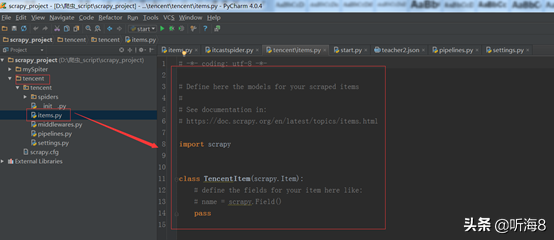
第二步:编写 items.py 文件,设置好需要保存的数据字段。
import scrapy
class TencentItem(scrapy.Item):
# 职位名
positionname = scrapy.Field()
# 详情连接
positionlink = scrapy.Field()
# 职位类别
positionType = scrapy.Field()
# 招聘人数
peopleNum = scrapy.Field()
# 工作地点
workLocation = scrapy.Field()
# 发布时间
publishTime = scrapy.Field()

第三步:创建爬虫。
在 dos下切换到目录
D:爬虫_scriptscrapy_projecttencenttencentspiders
用命令 scrapy genspider tencents "tencent.com" 创建爬虫。
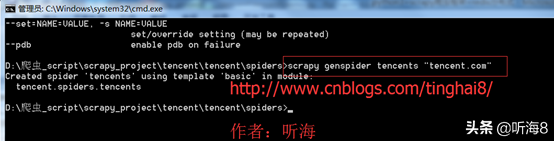
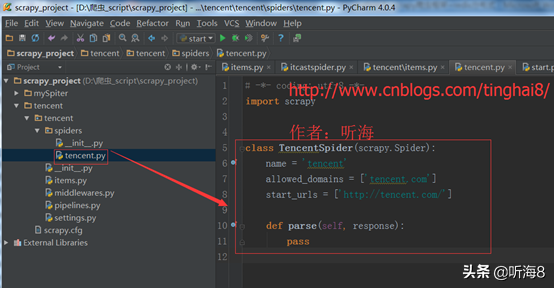
备注:因为用命令创建的时候,爬虫名称不能和域名tencent.com 一样,所以创建的时候,爬虫名为:tencents,创建完之后,可以把爬虫名修改成 tencent。
第四步:编写爬虫文件。
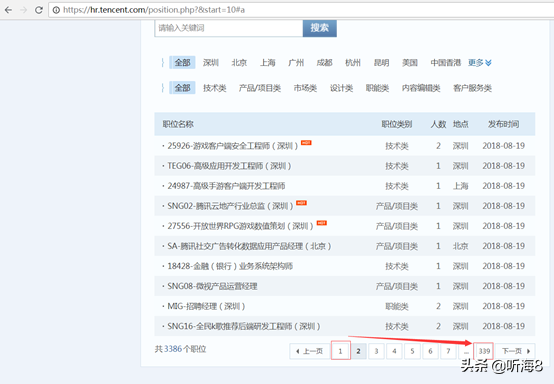
从图片中看到tencent招聘信息有339页。
第一页的链接地址:
https://hr.tencent.com/position.php?&start=0
第二页的链接地址:
https://hr.tencent.com/position.php?&start=10
最后一页的链接地址:
https://hr.tencent.com/position.php?&start=3380
通过分析我们得知,每一页的的链接地址start的值递增10,就是下一页的地址。

通过对页面的分析,得出需要保存的数据字段在页面上的位置。
info= response.xpath("//tr[@class='even'] | //tr[@class='odd']")
each in info
# 职位名
item['positionname'] = each.xpath("./td[1]/a/text()").extract()[0]
# 详情连接
item['positionlink'] = each.xpath("./td[1]/a/@href").extract()[0]
# 职位类别
item['positionType'] = each.xpath("./td[2]/text()").extract()[0]
# 招聘人数
item['peopleNum'] = each.xpath("./td[3]/text()").extract()[0]
# 工作地点
item['workLocation'] = each.xpath("./td[4]/text()").extract()[0]
# 发布时间
item['publishTime'] = each.xpath("./td[5]/text()").extract()[0]
编写完整的爬虫文件。
import scrapy,sys,os
path = os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))))
#print(path)
sys.path.Append(path)
from tencent.items import TencentItem
class TencentpositionSpider(scrapy.Spider):
name = "tencent"
allowed_domains = ["tencent.com"]
url = "http://hr.tencent.com/position.php?&start="
offset = 0
start_urls = [url + str(offset)]
def parse(self, response):
info= response.xpath("//tr[@class='even'] | //tr[@class='odd']")
for each in info:
# 初始化模型对象
item = TencentItem()
item['positionname'] = each.xpath("./td[1]/a/text()").extract()[0]
# 详情连接
item['positionlink'] = each.xpath("./td[1]/a/@href").extract()[0]
# 职位类别
item['positionType'] = each.xpath("./td[2]/text()").extract()[0]
# 招聘人数
item['peopleNum'] = each.xpath("./td[3]/text()").extract()[0]
# 工作地点
item['workLocation'] = each.xpath("./td[4]/text()").extract()[0]
# 发布时间
item['publishTime'] = each.xpath("./td[5]/text()").extract()[0]
#将获取的数据交给管道文件 pipelines ,yield的作用是把一个函数当成一个生成器,程序每次执行到yield时,返回一个值,程序会先暂停,下次调用再返回一个值,程序会接着暂停....
yield item
if self.offset < 3390:
self.offset += 10
# 每次处理完一页的数据之后,重新发送下一页页面请求
# self.offset自增10,同时拼接为新的 url,并调用回调函数 self.parse 处理 Response
yield scrapy.Request(self.url + str(self.offset), callback = self.parse)
第五步:编写管道文件:TencentPipeline。
import json
class TencentPipeline(object):
# __init__方法是可选的,做为类的初始化方法
def __init__(self):
# 创建了一个 tencent.json 文件,用来保存数据
self.filename = open("tencent.json", "wb")
# process_item方法是必须写的,用来处理item数据
def process_item(self, item, spider):
text = json.dumps(dict(item), ensure_ascii = False) + ",n"
# 把数据写入到tencent.json 文件中,编码为:utf-8
self.filename.write(text.encode("utf-8"))
return item
# close_spider方法是可选的,结束时调用这个方法
def close_spider(self, spider):
self.filename.close()
第六步:修改 settings 文件。

在settings.py文件配置里指定刚才编写的管道文件名:TencentPipeline。

下载的数据比较多,需要设定一个下载延时时间,以免下载的数据不全。

设置爬虫请求的默认头信息。
第七步:运行爬虫。
在 dos下切换到目录
D:爬虫_scriptscrapy_projecttencenttencent 下
通过命令运行爬虫 :scrapy crawl tencent
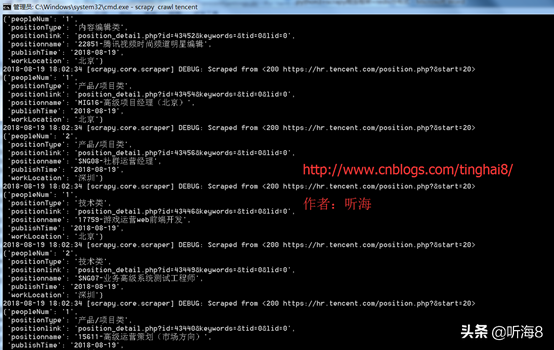
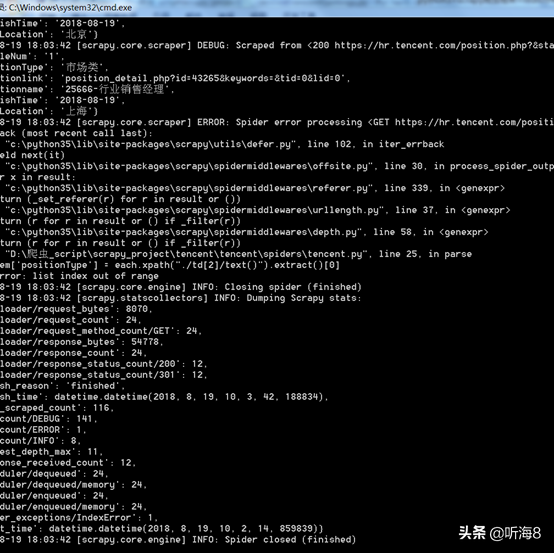
第八步:查看爬取的结果。
查看新建的tencent.json 数据文件。
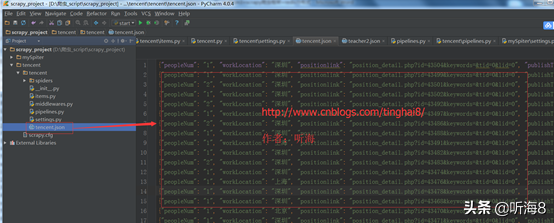
1.2 Scrapy 爬虫案例二
Scrapy 爬虫案例:斗鱼图片下载
案例步骤:
第一步:通过 Fiddler 进行手机抓包。
通过Fiddler抓包工具,可以抓取手机的网络通信,但前提是手机和电脑处于同一局域网内(WI-FI或热点),然后进行以下设置:
用 Fiddler 对 Android 应用进行抓包的设置:
1、打开 Fiddler 设置(Tools->options)。
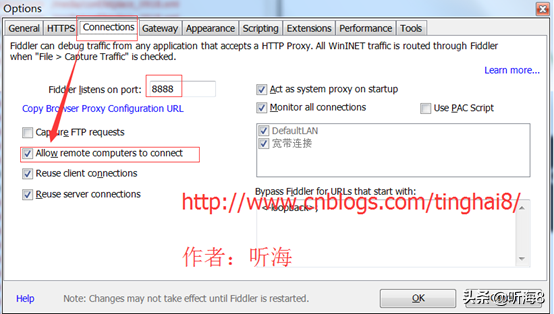
2、在 Connections 里设置允许连接远程计算机,确认后重新启动 Fiddler 。
3、在命令提示符下输入 ipconfig 查看本电脑 IP。
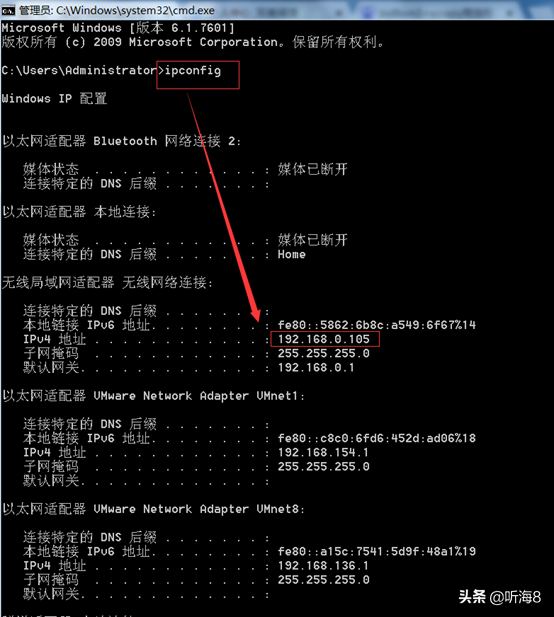
4、打开 Android 设备的“设置”->“WLAN”,找到你要连接的网络,进入该网络。
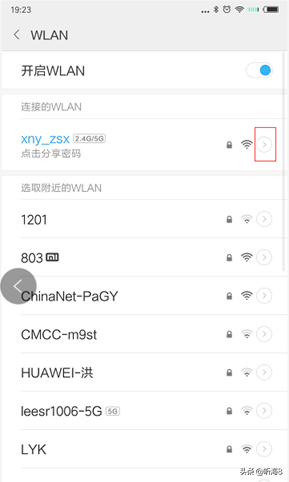
5、在“代理”后面的输入框选择“手动”,在“代理服务器主机名”后面的输入框输入电脑的 ip 地址,在“代理服务器端口”后面的输入框输入 8888,然后点击“保存”按钮。
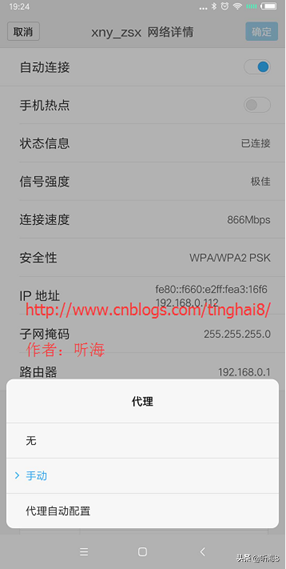
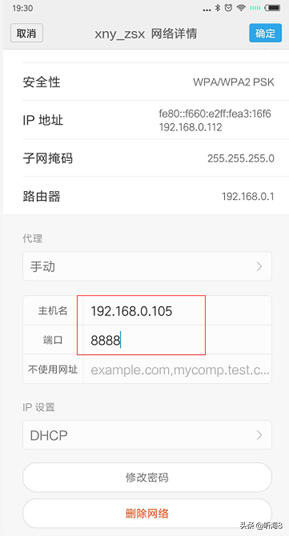
6、启动 Android 设备中的浏览器,访问网页即可在 Fiddler 中可以看到完成的请求和响应数据。
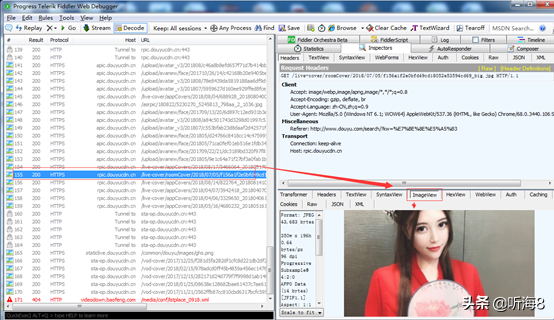
通过抓包,我们可以看出,请求返回的每页图片数据是一个 json 格式的文件,我们找到每页对应的 json 文件即可。
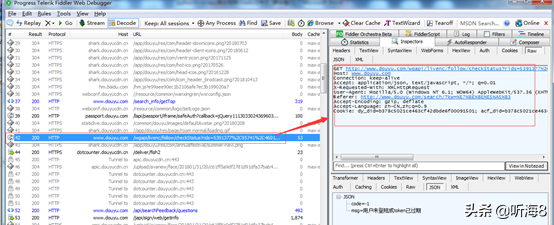
第二步:每页请求返回的json数据分析。
第 1 页 URL 地址:
http://capi.douyucdn.cn/api/v1/getVerticalRoom?limit=20&offset=0
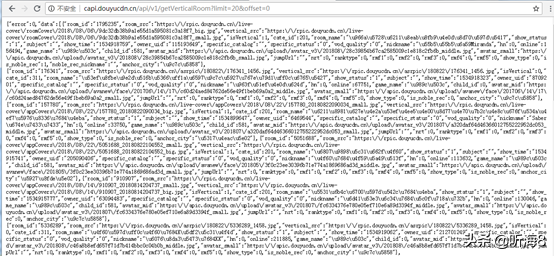
第 2 页 URL 地址:
http://capi.douyucdn.cn/api/v1/getVerticalRoom?limit=20&offset=20

第 20 页地址:
http://capi.douyucdn.cn/api/v1/getVerticalRoom?limit=20&offset=400
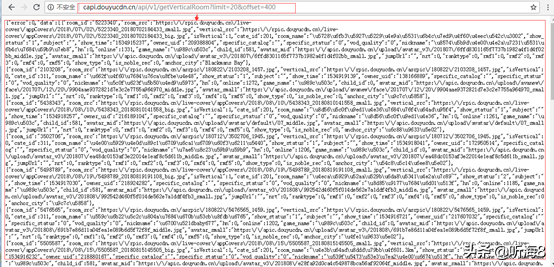
第 35 页地址:
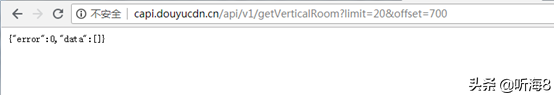
显示如上,表示数据没有35页。
【limit】:表示每页20条数据,每页偏移量是20。
【offset】:表示页数。
把第 1 页的返回的 json 格式的数据拷贝,通过 json 在线解析工具(https://www.json.cn/)对数据进行解析,如下:

其中每一页20条数据,每条数据显示如下:
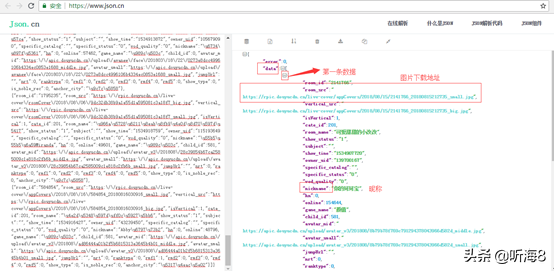
第三步:创建 scrapy 爬虫项目。
在 dos下切换到目录
D:scrapy_project
新建一个新的爬虫项目:scrapy startproject douyu
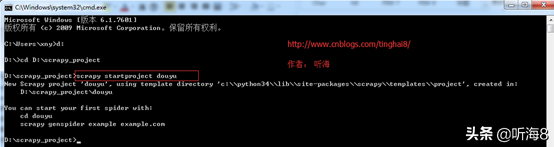
第四步:明确需要爬取的字段,编写 items 文件。
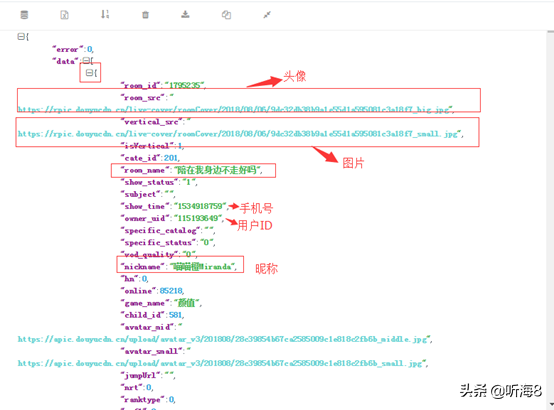
对于上面的信息,我们只抓取 2 个字段(昵称和图片链接)。
为了保存图片,还需增加一个图片保存路径的字段。
编写 Items.py 文件。
import scrapy
class DouyuItem(scrapy.Item):
# define the fields for your item here like:
#昵称
nickname = scrapy.Field()
#图片下载链接
imagelink = scrapy.Field()
#图片下载的本地保存路径
imagePath = scrapy.Field()
第五步:新建爬虫,编写爬虫文件。
在 DOS 下切换目录
D:scrapy_projectdouyudouyuspiders
执行命令新建爬虫命令:
scrapy genspider douyuMM "capi.douyucdn.cn"
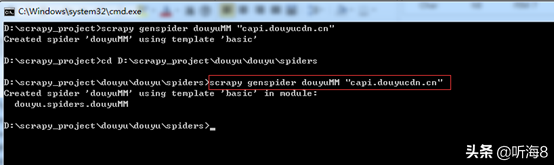
编写爬虫文件。
import scrapy,sys,os
import json
path = os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))))
sys.path.append(path)
from douyu.items import DouyuItem
class DouyummSpider(scrapy.Spider):
#爬虫名
name = "douyuMM"
#允许爬虫作用的范围
allowed_domains = ["capi.douyucdn.cn"]
# URL 变量
offset = 0
#基础的 URL
url = "http://capi.douyucdn.cn/api/v1/getVerticalRoom?limit=20&offset="
# 爬虫起始的url
start_urls = [url + str(offset)]
def parse(self, response):
# 请求返回的数据是json格式,需要把json格式的数据转换为 Python 格式,data 段是列表
data = json.loads(response.text)["data"]
for each in data:
#定义一个Item 对象,用来保存数据的
item = DouyuItem()
# 取 data 列表中的值,放到 Item 对象中
item["nickname"] = each["nickname"]
item["imagelink"] = each["vertical_src"]
## 将获取的数据交给管道文件 pipelines ,yield的作用是把一个函数当成一个生成器,程序每次执行到yield时,返回一个值,程序会先暂停,下次调用再返回一个值,程序会接着暂停....
yield item
if self.offset < 400:
self.offset += 20
# 每次处理完一页的数据之后,重新发送下一页页面请求
# self.offset自增20,同时拼接为新的 url,并调用回调函数 self.parse 处理 Response
yield scrapy.Request(self.url + str(self.offset), callback = self.parse)
第六步:分析 pipelines 管道文件处理的数据类型。
第一个案例讲的 pipelines 管道文件处理的是 html 页面的静态文本,这个案例需要处理的是图片,需要把图片下载下来,需要对 Settings.py 文件进行相应的配置。
第七步:修改 Settings.py 文件。
1、修改默认的请求信息(手机端浏览器)。
# Override the default request headers:
DEFAULT_REQUEST_HEADERS = {
"User-Agent" : "DYZB/1 CFNetwork/808.2.16 Darwin/16.3.0",
}
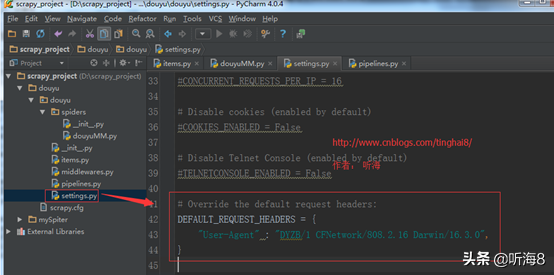
2.设置管道文件(管道文件类型:ImagesPipeline)
ImagesPipeline 是专门处理图片的管道文件。
# Configure item pipelines
# See https://doc.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/item-pipeline.html
ITEM_PIPELINES = {
'douyu.pipelines.ImagesPipeline': 300,
}
3.增加一个存储下载图片的本地路径。
IMAGES_STORE = "D:/scrapy_project/douyu/Images"
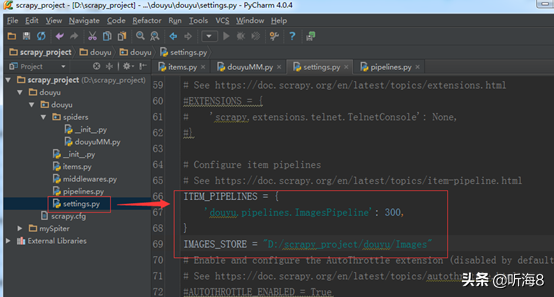
后续可以在 pipelines 管道文件程序里直接使用自己定义的图片存储路径变量。
第七步:编写 pipelines 管道文件。
pipelines 管道文件有专门处理 files(文件)、images(图片)、media(视频)3个库。
C:Python34Libsite-packagesscrapypipelines
查看 images.py 源码。
"""
Images Pipeline
See documentation in topics/media-pipeline.rst
"""
import functools
import hashlib
import six
try:
from cStringIO import StringIO as BytesIO
except ImportError:
from io import BytesIO
from PIL import Image
from scrapy.utils.misc import md5sum
from scrapy.utils.python import to_bytes
from scrapy.http import Request
from scrapy.settings import Settings
from scrapy.exceptions import DropItem
#TODO: from scrapy.pipelines.media import MediaPipeline
from scrapy.pipelines.files import FileException, FilesPipeline
class NoimagesDrop(DropItem):
"""Product with no images exception"""
class ImageException(FileException):
"""General image error exception"""
class ImagesPipeline(FilesPipeline):
"""Abstract pipeline that implement the image thumbnail generation logic
"""
MEDIA_NAME = 'image'
# Uppercase attributes kept for backward compatibility with code that subclasses
# ImagesPipeline. They may be overridden by settings.
MIN_WIDTH = 0
MIN_HEIGHT = 0
EXPIRES = 90
THUMBS = {}
DEFAULT_IMAGES_URLS_FIELD = 'image_urls'
DEFAULT_IMAGES_RESULT_FIELD = 'images'
def __init__(self, store_uri, download_func=None, settings=None):
super(ImagesPipeline, self).__init__(store_uri, settings=settings,
download_func=download_func)
if isinstance(settings, dict) or settings is None:
settings = Settings(settings)
resolve = functools.partial(self._key_for_pipe,
base_class_name="ImagesPipeline",
settings=settings)
self.expires = settings.getint(
resolve("IMAGES_EXPIRES"), self.EXPIRES
)
if not hasattr(self, "IMAGES_RESULT_FIELD"):
self.IMAGES_RESULT_FIELD = self.DEFAULT_IMAGES_RESULT_FIELD
if not hasattr(self, "IMAGES_URLS_FIELD"):
self.IMAGES_URLS_FIELD = self.DEFAULT_IMAGES_URLS_FIELD
self.images_urls_field = settings.get(
resolve('IMAGES_URLS_FIELD'),
self.IMAGES_URLS_FIELD
)
self.images_result_field = settings.get(
resolve('IMAGES_RESULT_FIELD'),
self.IMAGES_RESULT_FIELD
)
self.min_width = settings.getint(
resolve('IMAGES_MIN_WIDTH'), self.MIN_WIDTH
)
self.min_height = settings.getint(
resolve('IMAGES_MIN_HEIGHT'), self.MIN_HEIGHT
)
self.thumbs = settings.get(
resolve('IMAGES_THUMBS'), self.THUMBS
)
@classmethod
def from_settings(cls, settings):
s3store = cls.STORE_SCHEMES['s3']
s3store.AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID = settings['AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID']
s3store.AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY = settings['AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY']
s3store.POLICY = settings['IMAGES_STORE_S3_ACL']
gcs_store = cls.STORE_SCHEMES['gs']
gcs_store.GCS_PROJECT_ID = settings['GCS_PROJECT_ID']
store_uri = settings['IMAGES_STORE']
return cls(store_uri, settings=settings)
def file_downloaded(self, response, request, info):
return self.image_downloaded(response, request, info)
def image_downloaded(self, response, request, info):
checksum = None
for path, image, buf in self.get_images(response, request, info):
if checksum is None:
buf.seek(0)
checksum = md5sum(buf)
width, height = image.size
self.store.persist_file(
path, buf, info,
meta={'width': width, 'height': height},
headers={'Content-Type': 'image/jpeg'})
return checksum
def get_images(self, response, request, info):
path = self.file_path(request, response=response, info=info)
orig_image = Image.open(BytesIO(response.body))
width, height = orig_image.size
if width < self.min_width or height < self.min_height:
raise ImageException("Image too small (%dx%d < %dx%d)" %
(width, height, self.min_width, self.min_height))
image, buf = self.convert_image(orig_image)
yield path, image, buf
for thumb_id, size in six.iteritems(self.thumbs):
thumb_path = self.thumb_path(request, thumb_id, response=response, info=info)
thumb_image, thumb_buf = self.convert_image(image, size)
yield thumb_path, thumb_image, thumb_buf
def convert_image(self, image, size=None):
if image.format == 'PNG' and image.mode == 'RGBA':
background = Image.new('RGBA', image.size, (255, 255, 255))
background.paste(image, image)
image = background.convert('RGB')
elif image.mode == 'P':
image = image.convert("RGBA")
background = Image.new('RGBA', image.size, (255, 255, 255))
background.paste(image, image)
image = background.convert('RGB')
elif image.mode != 'RGB':
image = image.convert('RGB')
if size:
image = image.copy()
image.thumbnail(size, Image.ANTIALIAS)
buf = BytesIO()
image.save(buf, 'JPEG')
return image, buf
def get_media_requests(self, item, info):
return [Request(x) for x in item.get(self.images_urls_field, [])]
def item_completed(self, results, item, info):
if isinstance(item, dict) or self.images_result_field in item.fields:
item[self.images_result_field] = [x for ok, x in results if ok]
return item
def file_path(self, request, response=None, info=None):
## start of deprecation warning block (can be removed in the future)
def _warn():
from scrapy.exceptions import ScrapyDeprecationWarning
import warnings
warnings.warn('ImagesPipeline.image_key(url) and file_key(url) methods are deprecated, '
'please use file_path(request, response=None, info=None) instead',
category=ScrapyDeprecationWarning, stacklevel=1)
# check if called from image_key or file_key with url as first argument
if not isinstance(request, Request):
_warn()
url = request
else:
url = request.url
# detect if file_key() or image_key() methods have been overridden
if not hasattr(self.file_key, '_base'):
_warn()
return self.file_key(url)
elif not hasattr(self.image_key, '_base'):
_warn()
return self.image_key(url)
## end of deprecation warning block
image_guid = hashlib.sha1(to_bytes(url)).hexdigest() # change to request.url after deprecation
return 'full/%s.jpg' % (image_guid)
def thumb_path(self, request, thumb_id, response=None, info=None):
## start of deprecation warning block (can be removed in the future)
def _warn():
from scrapy.exceptions import ScrapyDeprecationWarning
import warnings
warnings.warn('ImagesPipeline.thumb_key(url) method is deprecated, please use '
'thumb_path(request, thumb_id, response=None, info=None) instead',
category=ScrapyDeprecationWarning, stacklevel=1)
# check if called from thumb_key with url as first argument
if not isinstance(request, Request):
_warn()
url = request
else:
url = request.url
# detect if thumb_key() method has been overridden
if not hasattr(self.thumb_key, '_base'):
_warn()
return self.thumb_key(url, thumb_id)
## end of deprecation warning block
thumb_guid = hashlib.sha1(to_bytes(url)).hexdigest() # change to request.url after deprecation
return 'thumbs/%s/%s.jpg' % (thumb_id, thumb_guid)
# deprecated
def file_key(self, url):
return self.image_key(url)
file_key._base = True
# deprecated
def image_key(self, url):
return self.file_path(url)
image_key._base = True
# deprecated
def thumb_key(self, url, thumb_id):
return self.thumb_path(url, thumb_id)
thumb_key._base = True
有兴趣的同学,可以完整的解读下。
本案例中用到其中2个方法:
1. get_media_requests(self, item, info)
2. item_completed(self, results, item, info)
编写 pipelines 管道文件
#get_media_requests(self, item, info)方法用到 scrapy.Request(image_url)下载图片,所以需要导入 scrapy 库
import scrapy
# 通过 get_project_settings 获取项目的 settings 文件
from scrapy.utils.project import get_project_settings
# 导入 ImagesPipeline 类
from scrapy.pipelines.images import ImagesPipeline
import os
# ImagesPipeline 继承 ImagesPipeline 父类,重写 ImagesPipeline 类
class ImagesPipeline(ImagesPipeline):
# 获取settings文件里设置的变量值
IMAGES_STORE = get_project_settings().get("IMAGES_STORE")
def get_media_requests(self, item, info):
# 爬虫爬取到的数据:图片的链接
image_url = item["imagelink"]
# 发下载图片的请求,参数是爬虫爬取到的图片地址。发送请求之后,会通过下面的item_completed(self, result, item, info)方法进行数据的处理。
yield scrapy.Request(image_url)
def item_completed(self, result, item, info):
# 这个是 item_completed()固定的写法,获取图片的名字
image_path = [x["path"] for ok, x in result if ok]
#对下载的文件重命名
os.rename(self.IMAGES_STORE + "/" + image_path[0], self.IMAGES_STORE + "/" + item["nickname"] + ".jpg")
item["imagePath"] = self.IMAGES_STORE + "/" + item["nickname"]
return item
第八步:启动爬虫,爬取数据。
在 dos下切换到目录
D:scrapy_projectdouyudouyu 下
通过命令运行爬虫 :scrapy crawl douyuMM

下载完成。
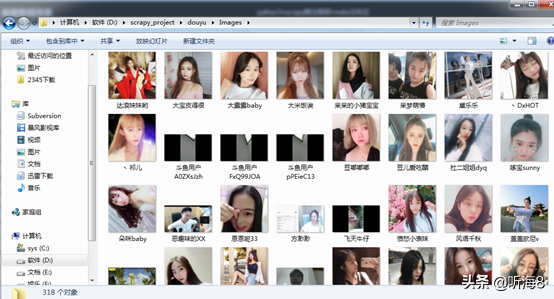
第九步:检查爬取的数据。
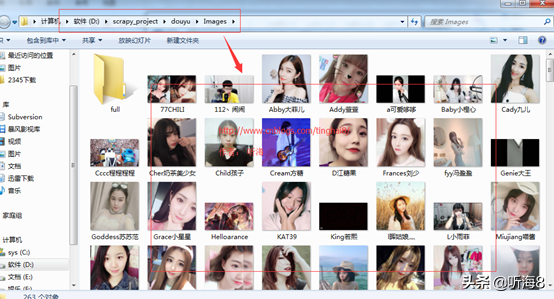
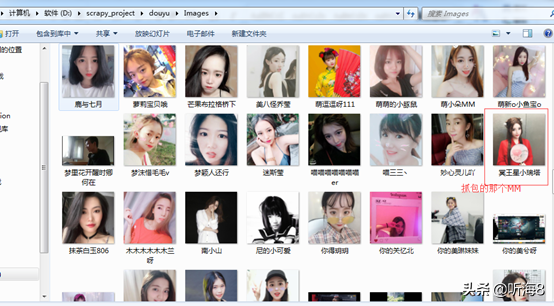
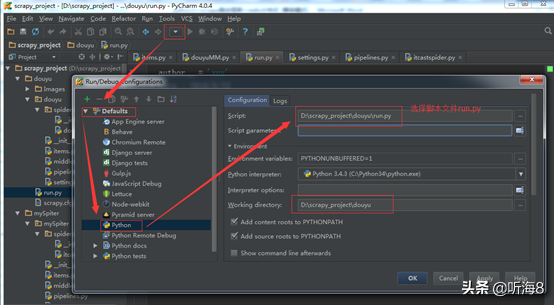
第十步:在项目根目录下新建 run.py 文件,便于PyCharm 下运行调试脚本。
在 D:scrapy_projectdouyudouyu 下。
新建 run.py 文件。
编写 run.py 文件。
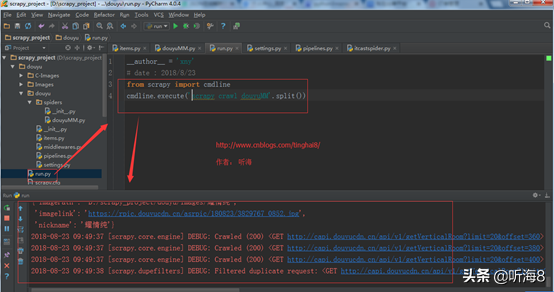
from scrapy import cmdline
cmdline.execute('scrapy crawl douyu'.split())
设置 run.py 文件运行环境。
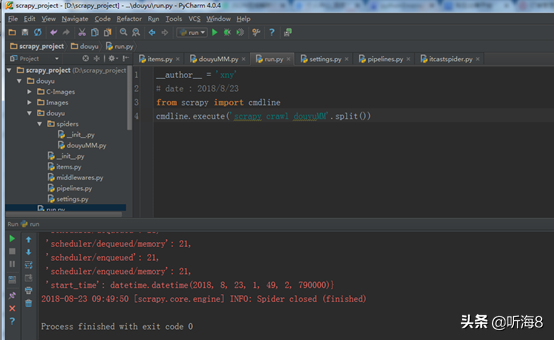
第十一步:在 PyCharm 下运行,查看运行结果。
1.3 Scrapy 爬虫案例基础篇小结汇总
1、2个案例爬虫文件里的 scrapy 类都是基于scrapy.Spider 基础类,Spider类是 scrapy爬虫框架实现爬虫的其中一个类,后面还会讲到另外的一个类
scrapy.spiders.CrawlSpider 。
2、第一个案例的 pipelines 管道文件是处理 html 静态文件,第二个案例 pipelines 管道文件是处理下载图片的。