
众所周知,Redis是高性能的、基于内存的、k-v数据库。其强大的功能背后,存在着2种不同类型的事件驱动,包括:
文件事件是对相关的 fd 相关操作的封装,时间事件则是对定时任务相关操作的封装。Redis server通过文件事件来进行外部请求的处理与操作,通过时间事件来对系统内部产生的定时任务进行处理。(本文重点讲解文件事件相关的操作流程以及原理)
文中探讨的原理及源码基于Redis官方 v7.0 版本
在Redis源码中,涉及事件驱动相关的源码文件主要有以下几个(以ae作为文件名称前缀):
src
├── ae.c
├── ae.h
├── ae_epoll.c
├── ae_evport.c
├── ae_kqueue.c
└── ae_select.c
根据源码中注释(ae.c)可知 ae 的含义为 A simple event-driven。
/* A simple event-driven programming library. Originally I wrote this code
* for the Jim's event-loop (Jim is a Tcl interpreter) but later translated
* it in form of a library for easy reuse.
*/
一个简单的事件驱动编程库。最初我(作者:antirez)为Jim的事件循环(Jim是Tcl解释器)编写了这段代码,但后来将其转化为库形式以便于重用。
在Redis源码中存在多种i/o多路复用实现方式,如何选择使用哪种i/o多路复用实现呢?源码编译时选择不同的实现方式,即:Redis源码编译成二进制文件的时候来选择对应的实现方式,在源码可以看到蛛丝马迹。
代码文件: ae.c
#ifdef HAVE_EVPORT
#include "ae_evport.c"
#else
#ifdef HAVE_EPOLL
#include "ae_epoll.c"
#else
#ifdef HAVE_KQUEUE
#include "ae_kqueue.c"
#else
#include "ae_select.c"
#endif
#endif
#endif
从上面代码可知,在编译源码的预处理阶段,根据不同的编译条件(#ifdef/#else/#endif)来判断对应的宏是否定义(#define定义的常量)来加载实现逻辑。以epoll为例,若定义了 HAVE_EPOLL 宏,则加载 "ae_epoll.c" 文件。宏 "HAVE_EVPORT/HAVE_EPOLL/HAVE_KQUEUE" 分别对应不同的系统(或者说是对应的编译器)。
代码文件: config.h
#ifdef __sun
#include <sys/feature_tests.h>
#ifdef _DTRACE_VERSION
#define HAVE_EVPORT 1
#define HAVE_PSINFO 1
#endif
#endif
#ifdef __linux__
#define HAVE_EPOLL 1
#endif
#if (defined(__AppLE__) && defined(MAC_OS_X_VERSION_10_6)) || defined(__FreeBSD__) || defined(__OpenBSD__) || defined (_.NETBSD__)
#define HAVE_KQUEUE 1
#endif
假设,当前是linux系统,那么 宏__linux__ 又是从哪里来的呢?Linux环境下主要用gcc编译,借助 gcc -dM -E - < /dev/null 命令从获得相应的变量中可以看到其定义。
root@ivansli ~# gcc -dM -E - < /dev/null | grep __linux
#define __linux 1
#define __linux__ 1
即:Redis源码会根据编译器来判断应该把源码编译成对应平台(或者是通用平台,性能会有所下降)运行的二进制可执行程序。
aeEventLoop 结构体如下所示:
/* State of an event based program 事件驱动程序的状态 */
typedefstruct aeEventLoop {
int maxfd; /* highest file descriptor currently registered. 当前已注册的最高文件描述符 */
int setsize; /* max number of file descriptors tracked. [events/fired数组的大小] */
longlong timeEventNextId; /* 时间事件的下一个ID */
/* events/fired 都是数组 */
/* events 数组,下标含义:为某个fd。fd=>aeFileEvent,即 文件描述符=>文件事件 */
/* fired 为 io多路复用返回的数组,每一个值为就绪的fd */
/* 通过 fired 中的 fd 去 events 查找对应的事件信息(事件信息包含conn) */
aeFileEvent *events; /* Registered events 已注册事件,数组 */
aeFiredEvent *fired; /* Fired events 触发的事件,数组 */
aeTimeEvent *timeEventHead; /* 时间事件,链表 */
int stop; /* 停止事件循环 */
void *apidata; /* This is used for polling API specific data. 这用于获取特定的API数据,aeApiState *state 包含io多路复用fd等字段 */
aeBeforeSleepProc *beforesleep;
aeBeforeSleepProc *aftersleep;
int flags;
} aeEventLoop;
aeEventLoop 结构体核心字段以及相关交互如下图所示:
// ae_epoll.c
typedefstruct aeApiState {/* 在 aeApiCreate 中初始化,linux则在 ae_linux.c 文件 */
int epfd; /* io多路复用fd */
struct epoll_event *events;/* 就绪的事件数组 */
} aeApiState;
// ae_kqueue.c
typedefstruct aeApiState {
int kqfd;
struct kevent *events;
/* Events mask for merge read and write event.
* To reduce memory consumption, we use 2 bits to store the mask
* of an event, so that 1 byte will store the mask of 4 events. */
char *eventsMask;
} aeApiState;
// ae_evport.c
typedefstruct aeApiState {
int portfd; /* event port */
uint_t npending; /* # of pending fds */
int pending_fds[MAX_EVENT_BATCHSZ]; /* pending fds */
int pending_masks[MAX_EVENT_BATCHSZ]; /* pending fds' masks */
} aeApiState;
// ae_select.c
typedefstruct aeApiState {
fd_set rfds, wfds;
/* We need to have a copy of the fd sets as it's not safe to reuse
* FD sets after select(). */
fd_set _rfds, _wfds;
} aeApiState;

aeEventLoop 相关操作方法签名如下所示(文件ae.h):
aeEventLoop *aeCreateEventLoop(int setsize);
void aeDeleteEventLoop(aeEventLoop *eventLoop);
void aeStop(aeEventLoop *eventLoop);
int aeCreateFileEvent(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, int fd, int mask, aeFileProc *proc, void *clientData);
void aeDeleteFileEvent(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, int fd, int mask);
int aeGetFileEvents(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, int fd);
void *aeGetFileClientData(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, int fd);
long long aeCreateTimeEvent(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, long long milliseconds,
aeTimeProc *proc, void *clientData, aeEventFinalizerProc *finalizerProc);
int aeDeleteTimeEvent(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, long long id);
int aeProcessEvents(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, int flags);
int aeWAIt(int fd, int mask, long long milliseconds);
void aeMain(aeEventLoop *eventLoop);
char *aeGetApiName(void);
void aeSetBeforeSleepProc(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, aeBeforeSleepProc *beforesleep);
void aeSetAfterSleepProc(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, aeBeforeSleepProc *aftersleep);
int aeGetSetSize(aeEventLoop *eventLoop);
int aeResizeSetSize(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, int setsize);
void aeSetDontWait(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, int noWait);
|
aeEventLoop事件处理核心方法 |
用途 |
调用i/o多路复用方法 |
epoll为例,调用方法 |
|
aeCreateEventLoop |
创建并初始化事件循环 |
aeApiCreate |
epoll_create() 默认水平触发 |
|
aeDeleteEventLoop |
删除事件循环 |
aeApiFree |
- |
|
aeCreateFileEvent |
创建文件事件 |
aeApiAddEvent |
epoll_ctl() EPOLL_CTL_ADD EPOLL_CTL_MOD |
|
aeDeleteFileEvent |
删除文件事件 |
aeApiDelEvent |
epoll_ctl() EPOLL_CTL_MOD EPOLL_CTL_DEL |
|
aeProcessEvents |
处理文件事件 |
aeApiPoll |
epoll_wait() |
|
aeGetApiName |
获取i/o多路复用的实现名称 |
aeApiName |
- |
客户端与服务端的连接建立过程,如下图所示:

TCP三次握手时,Linux内核会维护两个队列:
epoll相关处理方法与逻辑如下图所示:

基于epoll的i/o多路复用伪代码框架:
int main(){
lfd = socket(AF_INET,SOCK_STREAM,0); // 创建socket
bind(lfd, ...); // 绑定IP地址与端口
listen(lfd, ...); // 监听
// 创建epoll对象
efd = epoll_create(...);
// 把 listen socket 的事件管理起来
epoll_ctl(efd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, lfd, ...);
//事件循环
for (;;) {
size_t nready = epoll_wait(efd, ep, ...);
for (int i = 0; i < nready; ++i){
if(ep[i].data.fd == lfd){
fd = accept(listenfd, ...); //lfd上发生事件表示都连接到达,accept接收它
epoll_ctl(efd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, fd, ...);
}else{
//其它socket发生的事件都是读写请求、或者关闭连接
...
}
}
}
}

从上可知,Redis作为Server服务端在启动之后随时随刻监听着相关事件的发生。以linux为例,其处理过程与基于epoll的i/o多路复用伪代码框架基本相似,Redis源码中更多的是通过封装使其得到一个方便使用的库,库的底层包含了多种i/o多路复用实现方式。
以epoll为例,简化版的Redis事件驱动交互过程。
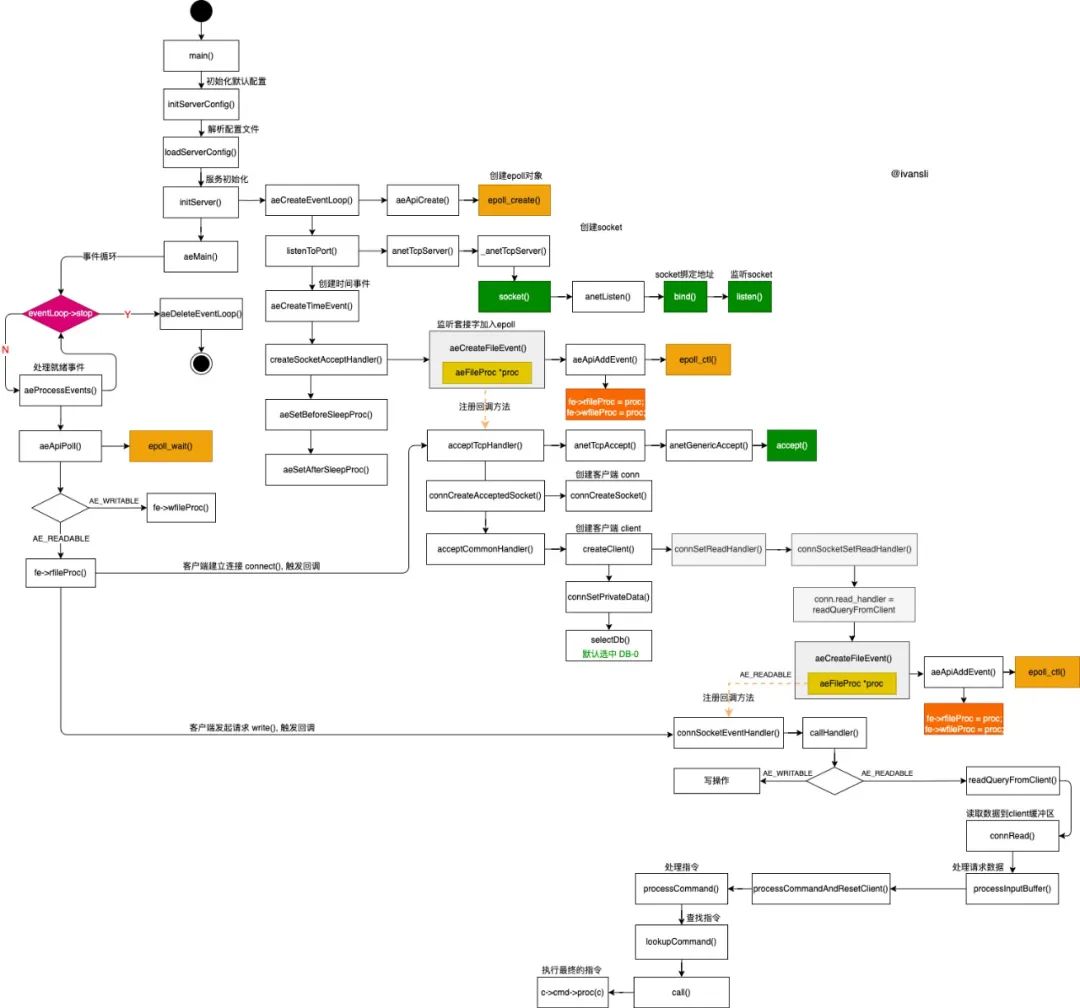
图中仅列出了核心方法,如有错误欢迎指正
Red括: 针对不同的 fd 注册 AE_READABLE/AE_WRITABLE 类型的回调方法,同时把 fd 添加到 epoll 中。当 fd 关心的事件触发之后,执行对应回调方法(主要针对 可读/可写/时间事件 3种类型的事件进行处理)。Redis 中 epoll 使用的触发方式为 LT 水平触发,意味着数据一次性没有处理完,下次 epoll_wait() 方法还会返回对应fd,直到处理完毕,对于客户端一次性发起批量处理多条命令的操作非常有益,减少对其他指令的阻塞时间。