
欢迎来到写代码那些事 !本教程将带您逐步深入了解使用 PyQt5 创建丰富、交互性强的图形用户界面(GUI)应用程序。无论您是新手还是有经验的开发者,通过本教程,您将学会如何利用 PyQt5 来构建现代化的用户界面,实现用户友好的交互体验。全文9387字,请您耐心读完
PyQt5 和 Tkinter 都是 Python/ target=_blank class=infotextkey>Python 中常用的 GUI(图形用户界面)库,用于创建各种窗口应用程序。它们有一些区别,下面是一些主要的区别点:
|
GUI库的来源 |
PyQt5:是一个Python绑定的Qt库,Qt是一个跨平台的C++ GUI开发框架,提供了丰富的GUI控件和功能 |
Tkinter:是Python的标准库,自带于Python,无需额外安装。 |
|
功能和控件 |
PyQt5:提供了丰富的GUI控件和功能,可以创建现代化的、功能丰富的应用程序。具有更多的内置控件和布局选项 |
Tkinter:功能相对较简单,提供了基本的GUI控件,适合创建简单的GUI界面 |
|
外观和主题 |
PyQt5:Qt库支持多样化的主题和样式,可以创建更具吸引力的用户界面 |
Tkinter:外观相对较为简单,主题和样式的自定义有限 |
|
学习曲线 |
PyQt5:由于功能丰富,学习曲线可能相对较陡峭,特别是对于新手来说 |
Tkinter:相对较简单,适合初学者入门,上手较快 |
|
跨平台性 |
PyQt5:支持跨平台,可以在多个操作系统上运行 |
Tkinter:同样支持跨平台,但在一些情况下可能需要进行更多的调整 |
|
社区支持和文档 |
PyQt5:拥有活跃的社区和完善的文档,有丰富的学习资源和示例 |
Tkinter:作为Python标准库的一部分,有许多教程和文档资源 |
|
第三方工具支持 |
PyQt5:与 Qt Designer 配合使用,可以通过可视化方式设计用户界面 |
Tkinter:可以使用 "tkinter.ttk" 模块扩展控件的外观 |
选择使用哪个库取决于您的需求和项目的复杂程度。如果您希望创建复杂的、现代化的用户界面,PyQt5 可能更适合。如果您只需要创建简单的GUI界面,或者希望使用标准库中自带的模块,那么 Tkinter 可能更合适。
PyQt5是一个Python绑定的Qt库,Qt是一个跨平台的GUI开发框架,用于创建图形用户界面。PyQt5提供了丰富的GUI控件、图形效果和工具,使开发者能够轻松地创建现代化的、功能丰富的应用程序。
要使用PyQt5,首先需要安装它。可以使用以下命令通过pip来安装PyQt5:
pip install PyQt5在这个示例中,我们将创建一个简单的PyQt5应用,显示一个窗口并在窗口中显示一个标签。
import sys
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMAInWindow, QLabel
# 创建应用程序对象
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
# 创建主窗口
window = QMainWindow()
window.setWindowTitle("My First PyQt5 App")
window.setGeometry(100, 100, 300, 200) # 设置窗口位置和大小
# 创建一个标签控件
label = QLabel("Hello, PyQt5!", window)
label.setGeometry(100, 50, 200, 30) # 设置标签位置和大小
# 显示窗口
window.show()
# 启动应用程序事件循环
sys.exit(app.exec_())
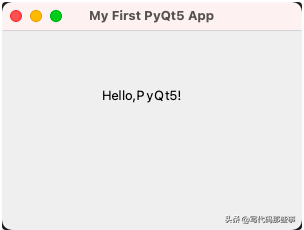
在这个示例中,我们使用了QApplication、QMainWindow和QLabel等控件。我们创建了一个应用程序对象,然后创建一个主窗口,设置了窗口的标题和位置大小。接着,我们创建了一个标签控件,设置了标签的文本、位置和大小。最后,通过调用show()方法显示窗口,并通过app.exec_()启动应用程序的事件循环。
创建了一个简单的PyQt5应用后,让我们熟悉一下基本的结构:
在PyQt5中,有许多常见的控件可供使用,以下是一些常见的控件以及它们的简要介绍:
在PyQt5中,布局管理器用于管理和排列控件的位置和大小,以便实现界面的布局。常见的布局管理器包括:
使用布局管理器可以避免手动设置每个控件的位置和大小,使界面布局更加灵活和自动化。例如,使用垂直布局可以将多个控件依次垂直排列,而使用网格布局可以将控件放置在二维网格中。
在PyQt5中,可以通过设置控件的属性和样式来自定义控件的外观和行为。一些常见的控件属性和方法包括:
例如,要设置按钮的文本和样式:
button = QPushButton("Click Me")
button.setGeometry(100, 100, 100, 30)
button.setStyleSheet("background-color: blue; color: white;")事件
事件是用户与应用程序交互时发生的动作,例如鼠标点击、键盘按键、窗口关闭等。每个控件都能够接收和处理各种事件。当事件发生时,PyQt5会自动触发相应的事件处理函数,也称为事件处理器。
信号与槽
信号是控件发出的消息,它表示某个事件已经发生。槽是一个函数,用于响应信号。通过将信号与槽进行连接,可以实现控件之间的通信和交互。当信号触发时,与之连接的槽函数会被调用。
要实现用户交互与响应,首先需要将控件的信号与回调函数(也就是槽函数)进行绑定。通过这种方式,当信号触发时,相应的回调函数将会被调用。
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow, QPushButton
app = QApplication([])
window = QMainWindow()
window.setWindowTitle("Event Handling Example")
window.setGeometry(100, 100, 300, 200)
button = QPushButton("Click Me", window)
button.setGeometry(100, 50, 100, 30)
# 定义一个回调函数
def on_button_click():
print("Button clicked!")
# 将按钮的clicked信号与回调函数绑定
button.clicked.connect(on_button_click)
window.show()
app.exec_()
在上面的示例中,我们创建了一个按钮控件,并定义了一个名为on_button_click的回调函数。然后,通过button.clicked.connect(on_button_click)将按钮的clicked信号与该回调函数进行绑定。当按钮被点击时,回调函数将会被调用,输出"Button clicked!"。
通过绑定控件的信号与回调函数,可以实现丰富的用户交互与响应功能。例如,按钮点击、文本框输入、滑块拖动等操作都可以通过信号与槽的机制来实现。这使得应用程序能够根据用户的操作做出相应的反应,提升了用户体验。
通过深入理解事件、信号和槽的概念,您可以构建交互性强、用户友好的GUI应用程序。在后续的教程中,我们将探讨更多不同类型的控件和事件,以及如何灵活地使用信号与槽来实现各种交互功能
在PyQt5中,可以使用QMainWindow来创建主窗口,使用QDialog来创建子窗口。以下是创建主窗口和子窗口的示例:
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow, QDialog, QPushButton
app = QApplication([])
# 创建主窗口
main_window = QMainWindow()
main_window.setWindowTitle("Main Window")
main_window.setGeometry(100, 100, 800, 600)
main_window.show()
app.exec_()
# 创建子窗口
main_window = QMainWindow()
main_window.setWindowTitle("Main Window")
main_window.setGeometry(100, 100, 800, 600)
mdi_area = QMdiArea(main_window)
main_window.setCentralWidget(mdi_area)
sub_window = QMdiSubWindow()
sub_window.setWidget(QPushButton("Sub Window Content"))
mdi_area.addSubWindow(sub_window)
main_window.show()
app.exec_()PyQt5提供了各种对话框,用于与用户进行交互并获取输入。其中,QInputDialog可以用于弹出输入对话框:
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow, QPushButton, QInputDialog
app = QApplication([])
main_window = QMainWindow()
main_window.setWindowTitle("Input Dialog Example")
main_window.setGeometry(100, 100, 400, 300)
def show_input_dialog():
text, ok = QInputDialog.getText(main_window, "Input Dialog", "Enter your name:")
if ok:
print("User's name:", text)
button = QPushButton("Show Input Dialog", main_window)
button.setGeometry(100, 100, 200, 30)
button.clicked.connect(show_input_dialog)
main_window.show()
app.exec_()在上面的示例中,点击"Show Input Dialog"按钮会弹出一个输入对话框,用户可以在对话框中输入内容。当用户点击确定后,输入的内容将会被打印出来。
除了内置的对话框外,您还可以自定义对话框和消息框,以满足特定的需求。自定义对话框通常是通过创建继承自QDialog的类来实现,然后在该类中添加自定义的控件和逻辑。
自定义消息框可以通过QMessageBox来创建,您可以设置消息框的图标、按钮和内容。以下是一个简单的示例:
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow, QPushButton, QMessageBox
app = QApplication([])
main_window = QMainWindow()
main_window.setWindowTitle("Message Box Example")
main_window.setGeometry(100, 100, 400, 300)
def show_message_box():
msg_box = QMessageBox()
msg_box.setIcon(QMessageBox.Information)
msg_box.setText("This is a message box.")
msg_box.setWindowTitle("Message Box")
msg_box.setStandardButtons(QMessageBox.Ok | QMessageBox.Cancel)
msg_box.setDefaultButton(QMessageBox.Ok)
result = msg_box.exec_()
if result == QMessageBox.Ok:
print("User clicked Ok")
else:
print("User clicked Cancel")
button = QPushButton("Show Message Box", main_window)
button.setGeometry(100, 100, 200, 30)
button.clicked.connect(show_message_box)
main_window.show()
app.exec_()
在上述示例中,点击"Show Message Box"按钮会弹出一个自定义消息框,用户可以点击"Ok"或"Cancel"按钮进行选择。根据用户的选择,相应的消息会被打印出来。
通过创建自定义对话框和消息框,您可以根据需要实现更灵活和个性化的用户交互界面
在PyQt5中,可以使用QGraphicsView和QGraphicsscene来创建画布并绘制基本图形。
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow, QGraphicsView, QGraphicsScene
from PyQt5.QtCore import Qt
from PyQt5.QtGui import QPen, QColor
app = QApplication([])
main_window = QMainWindow()
main_window.setWindowTitle("Canvas Example")
main_window.setGeometry(100, 100, 800, 600)
scene = QGraphicsScene()
view = QGraphicsView(scene, main_window)
view.setAlignment(Qt.AlignLeft | Qt.AlignTop)
view.setGeometry(0, 0, 800, 600)
main_window.show()
app.exec_()
# 在Canvas上绘制线段
pen = QPen(QColor(255, 0, 0))
scene.addLine(100, 100, 300, 300, pen)
# 在Canvas上绘制矩形
pen = QPen(QColor(0, 0, 255))
scene.addRect(400, 100, 200, 150, pen)
# 在Canvas上绘制椭圆
pen = QPen(QColor(0, 255, 0))
scene.addEllipse(100, 400, 150, 100, pen)要在Canvas上制作简单的图表和图像展示,可以使用QGraphicsView和QGraphicsScene来实现。您可以通过绘制基本图形和添加文本等方式来展示图表和图像。
# 绘制柱状图
rect_item = scene.addRect(100, 100, 50, 200, pen)
rect_item.setBrush(QColor(0, 0, 255))
# 添加文本标签
text_item = scene.addText("Sales Data", QFont("Arial", 12))
text_item.setPos(100, 50)要实现自定义绘图与图形效果,您可以通过继承QGraphicsItem来创建自定义的图形项。您可以在图形项的paint()方法中实现绘制自定义图形和效果。
以下是一个简单的自定义图形项示例:
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QGraphicsItem
class CustomGraphicsItem(QGraphicsItem):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
def boundingRect(self):
return QRectF(0, 0, 100, 100)
def paint(self, painter, option, widget):
painter.setBrush(QColor(255, 0, 0))
painter.drawRect(0, 0, 100, 100)
然后,将自定义图形项添加到场景中:
pythonCopy codecustom_item = CustomGraphicsItem()
scene.addItem(custom_item)
通过自定义图形项,您可以实现各种自定义的绘图和图形效果,从而使Canvas展示更多个性化内容。在后续的教程中,您还可以了解如何通过绘制路径、添加图片和渲染特效来实现更多的图形效果。
在PyQt5中,可以使用QMenuBar和QMenu来添加菜单栏和上下文菜单。
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow, QMenuBar, QMenu
app = QApplication([])
main_window = QMainWindow()
main_window.setWindowTitle("Menu Example")
main_window.setGeometry(100, 100, 800, 600)
menu_bar = QMenuBar(main_window)
main_window.setMenuBar(menu_bar)
file_menu = QMenu("File", menu_bar)
menu_bar.addMenu(file_menu)
edit_menu = QMenu("Edit", menu_bar)
menu_bar.addMenu(edit_menu)
main_window.show()
app.exec_()
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow, QMenu
app = QApplication([])
main_window = QMainWindow()
main_window.setWindowTitle("Context Menu Example")
main_window.setGeometry(100, 100, 800, 600)
def show_context_menu(pos):
context_menu = QMenu(main_window)
context_menu.addAction("Copy")
context_menu.addAction("Cut")
context_menu.addAction("Paste")
context_menu.exec_(main_window.mapToGlobal(pos))
main_window.setContextMenuPolicy(Qt.CustomContextMenu)
main_window.customContextMenuRequested.connect(show_context_menu)
main_window.show()
app.exec_()可以使用QToolBar和QToolButton来创建工具栏和工具按钮。
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow, QToolBar, QAction, QToolButton
app = QApplication([])
main_window = QMainWindow()
main_window.setWindowTitle("Tool Bar Example")
main_window.setGeometry(100, 100, 800, 600)
tool_bar = QToolBar("Tool Bar", main_window)
main_window.addToolBar(tool_bar)
action1 = QAction("Action 1", main_window)
tool_bar.addAction(action1)
action2 = QAction("Action 2", main_window)
tool_bar.addAction(action2)
tool_button = QToolButton()
tool_button.setText("Tool Button")
tool_bar.addWidget(tool_button)
main_window.show()
app.exec_()
可以通过嵌套QMenu来实现多层级的菜单结构。
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow, QMenuBar, QMenu
app = QApplication([])
main_window = QMainWindow()
main_window.setWindowTitle("Multi-level Menu Example")
main_window.setGeometry(100, 100, 800, 600)
menu_bar = QMenuBar(main_window)
main_window.setMenuBar(menu_bar)
file_menu = QMenu("File", menu_bar)
menu_bar.addMenu(file_menu)
new_menu = QMenu("New", file_menu)
file_menu.addMenu(new_menu)
new_menu.addAction("File")
new_menu.addAction("Folder")
edit_menu = QMenu("Edit", menu_bar)
menu_bar.addMenu(edit_menu)
main_window.show()
app.exec_()
在PyQt5中,可以使用QLineEdit、QLabel等界面控件来显示数据,并使用setText()等方法进行数据绑定。
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow, QLabel
app = QApplication([])
main_window = QMainWindow()
main_window.setWindowTitle("Data Binding Example")
main_window.setGeometry(100, 100, 800, 600)
label = QLabel("Hello, World!", main_window)
label.setGeometry(100, 100, 200, 30)
# 将数据绑定到控件
data = "Data from Python"
label.setText(data)
main_window.show()
app.exec_()您可以使用QTableWidget和QListWidget等控件来显示数据。
pythonCopy codefrom PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow, QTableWidget, QTableWidgetItem
app = QApplication([])
main_window = QMainWindow()
main_window.setWindowTitle("Table and List Example")
main_window.setGeometry(100, 100, 800, 600)
table = QTableWidget(main_window)
table.setGeometry(100, 100, 300, 200)
table.setColumnCount(3)
table.setHorizontalHeaderLabels(["Name", "Age", "Gender"])
# 添加数据行
data = [("Alice", 25, "Female"), ("Bob", 30, "Male")]
for row, (name, age, gender) in enumerate(data):
table.insertRow(row)
table.setItem(row, 0, QTableWidgetItem(name))
table.setItem(row, 1, QTableWidgetItem(str(age)))
table.setItem(row, 2, QTableWidgetItem(gender))
main_window.show()
app.exec_()如果需要更复杂的数据展示,您可以自定义数据模型和视图。
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow, QListView, QStandardItemModel, QStandardItem
app = QApplication([])
main_window = QMainWindow()
main_window.setWindowTitle("Custom Model and View Example")
main_window.setGeometry(100, 100, 800, 600)
list_view = QListView(main_window)
list_view.setGeometry(100, 100, 200, 300)
# 创建自定义数据模型
model = QStandardItemModel()
list_view.setModel(model)
# 添加数据项
data = ["Item 1", "Item 2", "Item 3"]
for item_text in data:
item = QStandardItem(item_text)
model.appendRow(item)
main_window.show()
app.exec_()在PyQt5中,可以使用QThread来实现多线程操作,以避免在主线程中执行耗时的任务导致界面冻结和卡顿。
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow, QPushButton
from PyQt5.QtCore import QThread, pyqtSignal, Qt
import time
class WorkerThread(QThread):
finished = pyqtSignal()
def run(self):
for i in range(1, 6):
print(f"Processing task {i}")
time.sleep(1)
self.finished.emit()
app = QApplication([])
main_window = QMainWindow()
main_window.setWindowTitle("Multi-threading Example")
main_window.setGeometry(100, 100, 800, 600)
button = QPushButton("Start Task", main_window)
button.setGeometry(100, 100, 100, 30)
def start_task():
button.setEnabled(False)
worker_thread = WorkerThread()
worker_thread.finished.connect(task_finished)
worker_thread.start()
def task_finished():
button.setEnabled(True)
print("Task finished")
button.clicked.connect(start_task)
main_window.show()
app.exec_()PyQt5提供了QThreadPool用于管理线程池,可以并行执行多个任务以提升应用性能。
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow, QPushButton
from PyQt5.QtCore import QThreadPool, QRunnable, Qt
import time
class WorkerRunnable(QRunnable):
def run(self):
for i in range(1, 6):
print(f"Processing task {i}")
time.sleep(1)
app = QApplication([])
main_window = QMainWindow()
main_window.setWindowTitle("Thread Pool Example")
main_window.setGeometry(100, 100, 800, 600)
button = QPushButton("Start Task", main_window)
button.setGeometry(100, 100, 100, 30)
def start_task():
button.setEnabled(False)
worker_runnable = WorkerRunnable()
thread_pool.start(worker_runnable)
def task_finished():
button.setEnabled(True)
print("Task finished")
thread_pool = QThreadPool()
thread_pool.setMaxThreadCount(2) # 设置最大线程数为2
button.clicked.connect(start_task)
main_window.show()
app.exec_()通过使用QThread实现多线程操作和利用异步机制提升应用性能,您可以在应用中执行耗时任务而不影响主界面的响应。
在PyQt5中,您可以通过继承现有的控件类来创建自定义控件和组件。
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow, QWidget, QLabel
class CustomLabel(QLabel):
def __init__(self, text):
super().__init__(text)
self.setStyleSheet("color: blue; font-size: 20px;")
app = QApplication([])
main_window = QMainWindow()
main_window.setWindowTitle("Custom Widget Example")
main_window.setGeometry(100, 100, 800, 600)
custom_label = CustomLabel("Custom Label", main_window)
custom_label.setGeometry(100, 100, 200, 30)
main_window.show()
app.exec_()通过使用setStyleSheet()方法,您可以定制控件的外观和样式。
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow, QPushButton
app = QApplication([])
main_window = QMainWindow()
main_window.setWindowTitle("Custom Style Example")
main_window.setGeometry(100, 100, 800, 600)
button = QPushButton("Styled Button", main_window)
button.setGeometry(100, 100, 150, 50)
button.setStyleSheet("background-color: green; color: white; font-size: 16px;")
main_window.show()
app.exec_()您可以通过布局管理器、控件的层叠、动画效果等方法来实现复杂的界面效果。
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow, QWidget, QVBoxLayout, QLabel, QPushButton, QStackedWidget
from PyQt5.QtCore import Qt
app = QApplication([])
main_window = QMainWindow()
main_window.setWindowTitle("Complex UI Example")
main_window.setGeometry(100, 100, 800, 600)
central_widget = QWidget(main_window)
main_window.setCentralWidget(central_widget)
layout = QVBoxLayout()
central_widget.setLayout(layout)
label = QLabel("Welcome to PyQt5!", central_widget)
layout.addWidget(label, alignment=Qt.AlignCenter)
stacked_widget = QStackedWidget(central_widget)
layout.addWidget(stacked_widget)
page1 = QWidget()
page2 = QWidget()
stacked_widget.addWidget(page1)
stacked_widget.addWidget(page2)
button1 = QPushButton("Page 1", page1)
button2 = QPushButton("Page 2", page2)
stacked_widget.setCurrentIndex(0)
button1.clicked.connect(lambda: stacked_widget.setCurrentIndex(0))
button2.clicked.connect(lambda: stacked_widget.setCurrentIndex(1))
main_window.show()
app.exec_()
通过创建自定义控件和组件、定制控件的外观和样式,以及实现复杂界面效果,您可以定制出独特且富有创意的GUI应用程序。
本教程帮助您入门使用PyQt5创建各种类型的GUI应用程序。通过了解PyQt5的基础知识,您可以开始构建自己的GUI项目,并为用户提供出色的用户体验。无论您是初学者还是有经验的开发者,都能从本教程中获得有用的知识和技能,让您能够在Python中轻松构建功能丰富的图形界面应用程序。